1. Classification:
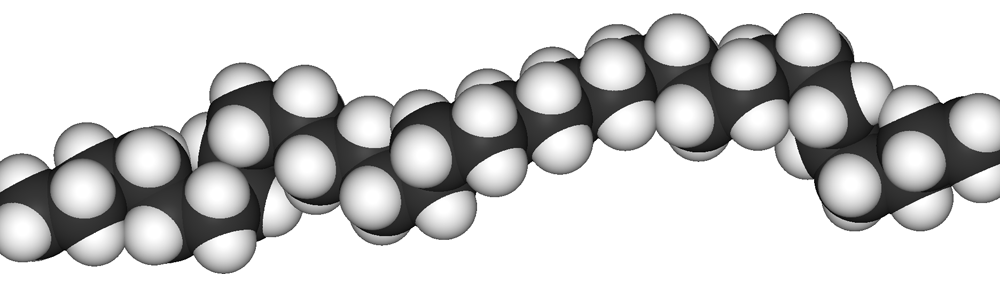
Polyethylene is a thermoplastic polymer consisting of long hydrocarbon chains ( chains of hydrogen and carbon atoms) where two Hydrogen atoms are bonded to each carbon atom. A polymer is a macromolecule which consists of thousands of atoms and its molecular masses can reach over a million.
Figure 1.1 3D Image of Polyethylene
2. Mechanism for the formation of Polyethylene
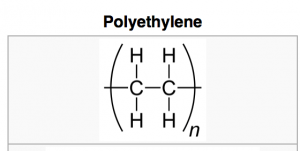
Figure 1.2 Each unit of Polyethylene
Polyethylene is produced by a process called Addition Polymerisation by linking each unit shown above in Figure 1.2 together multiple times. This mechanism will be elaborated in the Chemical Concept page.
3. Application in our daily life
There are many types of Polyethylene, but the most important ones are Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE) and High Density Polyethylene (HDPE). This would be further explained in the Chemical Concept page.
Polyethylene is commonly used in plastics that we use daily. This includes plastic bags, containers, pipes etc as shown in Figure 1.3.

Figure 1.3 Plastic bottles