Working principals behind an infusion pump
What is an infusion pump?
An infusion pump is a medical device that is used to administer a steady flow of medications and fluids to a patient over a set amount of time.
In the hospital setting, infusion pumps are commonly found in Intensive Care Units (ICUs), Neonatal Intensive Care Units (NICU) and Surgical and Oncology Centers.
Different infusion pump involves different mechanism in liquid transfusion, such as syringe pump which involves a piston mechanism while a balloon-pressure elastomeric pump would utilise pressure from a balloon to control liquid flow rate.
For our project, we will be exploring the use of peristaltic pumps (which contains rollers that compresses the tubing) to control the liquid flow rate.
How peristaltic infusion pumps work

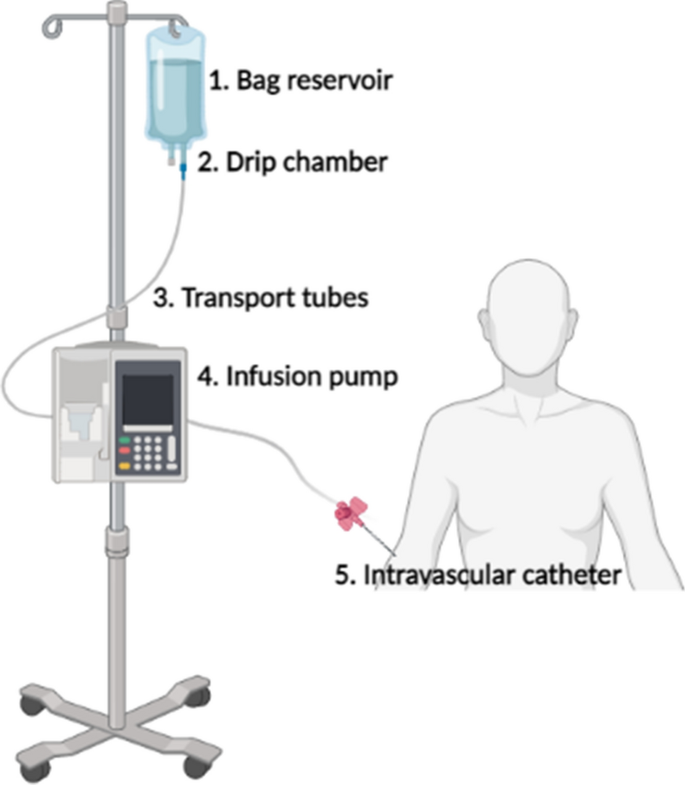
- Fluid reservoir: between 50ml – 1000ml
- Catheter / Plastic tubing: delivers fluid from reservoir to the patient; can be as long as 48” (~1.2m)
- Peristaltic pump
- User interface
- To program & monitor fluid delivery
Commonly used infusion liquids

- Common infusion solutions:
- Aqueous solutions of glucose (5 cg/g) (for treatment of carbohydrate & fluid depletion)
- Aqueous solutions of sodium chloride (0.9 cg/g) (also known as saline, used to treat dehydration)
- Aqueous solutions of sodium chloride (0.45 cg/g) (used for patients where there is an incompatibility of drugs to be administered / hypertensive patients)
- The above has similar viscosity and density to that of water, hence our pump which we calibrate using water as the reference liquid would be mainly applicable for the above solutions.
- For other commonly used infusion liquids that has much higher density and/or viscosity than water (such as Hespan® and Dextran 40® which are 4 times more viscous than water), this is an area we can explore in the future as our pump is mainly calibrated to the viscosity and density of water.
Precision & Accuracy of infusion pump
The accuracy of an infusion pump is based on how close the actual flow rate is to the programmed flow rate. Peristaltic infusion pumps used in hospital and ambulatory setting generally has an accuracy of ±2.5 – 6%, with a maximum flow rate of 250ml/hr.
Bicycle powered generator


- Presence of copper coils between 2 sets of magnets in the white component of above picture
- Pedaling rotates black gear which in turn causes magnets in white component to spin as they are connected
- Rotation of magnets result in a changing magnetic field which induces a current in the copper wires which can be used for recharging reusable batteries
Infusion pump delivery mechanisms – Stepper motor or traditional DC motor
Stepper Motor
DC motor
Traditional DC motors are much easier to code with. Only requires PWM to regulate the amount of current going into the motor to affect how fast it will spin and therefore the flowrate.
However, the most crucial factor of the DC motors are their low power draw relative to stepper motors. From our testing the DC motor can function with less than 1W of power, compared to close to 8w of the stepper motor. Especially since we want to target places where there might not be ready access to electricity and we rely on the battery that we charge up, every last bit of electricity is important, Thus the use of DC motors are still employed.
However one area where stepper motors far exceed DC motors are in their accuracy. Stepper motor moves ins ‘steps’ or the amount of angle specified, thus ensuring the same amount of peristaltic rollers movement every time. DC motors on the other hand can only be adjusted by their PWM, which will not only affect their speed, but also the torque they are able to produce.
One of the earilier methods we employed with the DC motor was to emulate that of a stepper motor, where we toggle the PWM to the motor, giving it short pulses, thus making it move in ‘steps’ as well. Using this method tied in with numerus testing and data would provide an adequate way of achieving an average flow rate that we want. However, ideally we hope to have a method that would have a continuous flow, as it prevents the issue of back pressure on the veins. Most, if not all medical infusion pumps are able to achieve this continuous flow rate as well.
Therefore to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the DC motor, which would always aim to achieve an instantaneous flowrate close or not equal to that of the target, a PID tuning system is used. The PID stands for:
P: Proportional
I: Integral
D: Derivative
These 3 aspects work together to ensure the accuracy of the of pump.
Proportional takes into account the current speed of the motor to decides whether it is enough to push the required flowrate
Integral looks at the performance and data from the start of operation, and then decides whether it is necessary to further tune and adjust the flow rate.
Lastly derivative aims to look into the further based on the current and past information and performance. This allows for the system to preemptively make any chances it might need before the any errors occur.
A PID controller requires a feedback mechanism, recording both the input and output values, allowing for a relation to be drawn between them. The arduino then inteprets these signals and adjusts the input accordingly to achieve the desired output. A rotary encoder will be used in this project to fulfill this role. Essentially, it is a very simple device that records the amount of rotations made by the pump and motor. Based on the specifications of said rotary encoder, we are then able to deduce the angular velocity of the motor too! Combined with experimently achieved results, we are able to make now draw a relation between angular velocity of the motor shaft with the flowrate of the pump.
However, this begs the question why not use a device like a flowmeter to directly measure the flowrate instead?
In our use cases, specifically in medical settings, slow flowrates, often less than 300ml/hr are often used. Traditional flowmeters are thus usually very inaccurate at detecting flowrates these slow. Medical setting flowmeters which ARE good for low flowrates on the other hand are often very expensive.
Moreover, IV tubings used in medical settings ARE meant to be disposable for sanitary reasons and patient safety. Therefore attaching these expensive medical grade flowmeters to each tubings would be very unfeasible.
Thus, the most practical way of recording our flowrates must be through an indirect method like the rotary encoder.
To work together with this PID controller, we must ensure proper calibration, so that the relation between the DC motor speed and flowrate is calculated properly. Other than our own set of testing, we have also added in a feature in the final product where the user themselves would be able to perform calibration on their own. This ensures that regardless of setup or fluids viscosity of positions, there SHOULD be a accurate way for the users themselves to tweak the pump accordingly to ensure consistent accurate flowrate.
