Permutation Test on Age
- Age ≤ 25 VS Age > 35
1) Experiment Set up
Null Hypothesis: Speaker who is 25 or below does not have better fluency score than those who are above 35
Alternative Hypothesis: Speaker who is 25 and below has better fluency score than those who are above 35
Number of permutation: 50000
Alpha level: 5%
2) Result and Analysis
p-value: 0.004
The p-value is smaller than the alpha value, we have to reject the null hypothesis. Hence, speaker whose age is 25 and below has better fluency score than those who are above 35.
- Age ≤ 25 VS 25 < Age ≤ 35
1) Experiment Set up
Null Hypothesis: Speaker who is 25 or below does not have better fluency score than those who are above 25 but below 35
Alternative Hypothesis: Speaker who is 25 and below has better fluency score than those who are above 25 but below 35
Number of permutation: 50000
Alpha level: 5%
2) Result and Analysis
p-value: 0.0003
The p-value is smaller than the alpha value, we have to reject the null hypothesis. Hence, speaker whose age is 25 and below has better fluency score than those who are above 25 but below 35.
- 25 < Age ≤ 35 VS Age > 35
1) Experiment Set up
Null Hypothesis: Speaker who is between 26 and 35 does not have better fluency score than those who are above 35
Alternative Hypothesis: Speaker who is between 26 and 35 has better fluency score than those who are above 35
Number of permutation: 50000
Alpha level: 5%
2) Result and Analysis
p-value: 0.002
The p-value is smaller than the alpha value, we have to reject the null hypothesis. Hence, speaker whose age is between 26 and 35 has better fluency score than those who are above 35.
- Result summary
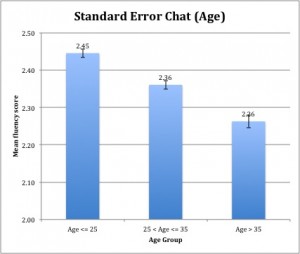
Figure 13 Standard Error Chart (Age)
According to the results from the above experiments, we can conclude that speaker who is 25 or below has the highest mean fluency score than speakers who are above 25. Figure 13 shows the summary of the results from the three experiments. Based on Figure 13, we can see that as the age increases, the fluency score obtained by the speaker tends to decrease. The standard error bar of each group does not overlap with each other; it can show that the difference in mean fluency score among the three age groups is significant.