What are fats?

Triglycerides are made up of 3 fatty acid molecules attached to a glycerol molecule (acts as a ‘backbone’ for the molecule) via ester bonds. Lipids are a type of In this blog, our focus is mainly on fats.
What is the difference between fats and oils?
Their physical states at room temperature will determine if they should be classified as ‘fats’ or ‘oils’. Fats are lipids that are solid at room temperature. Oils are lipids that are liquid at room temperature.
Physical Properties of Fat
Fats are non-volatile, slippery, greasy and soft. They have low melting temperatures and are water insoluble. They are usually found in products of animal origins.
Examples: Butter, meat, milk, cheese, omega-3 in salmon
Chemical properties
Prominent features of fatty acid molecules:
1) The long hydrocarbon fatty acid chains generally contains an even number of carbon atoms – ranging from 4 to 36, bonded in an unbranched chain. For saturated fatty acid chains,because the number of atoms attached to each carbon atom is the maximum of four, and all of these bonds are single bonds, the fatty acid termed ‘saturated’. For unsaturated fatty acid chains, if there is only one double bond, it is usually between the 9th and 10th carbon atom in the chain, where the carbon atom attached to the oxygen atoms is counted as the first carbon atom. If there is a second double bond, it usually occurs between the 12th and 13th carbon atoms, while a third is usually between the 15th and 16th.
2)
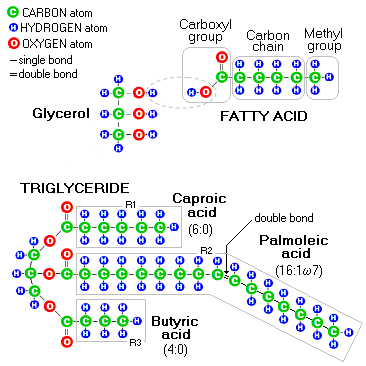
Carboxylic acid functional group at the end of each of the 3 fatty acid chains will react with the hydroxyl group on the glycerol molecule, to form one molecule of triglyceride and 3 molecules of water.
3) Lipids are insoluble in aqueous solutions as they are non-polar compounds.
When present in high concentrations, it will lead to the formation of larger fat droplets that will clog blood vessels. Thus, they must be transported as complexes of lipid and protein, called lipoproteins.

Due to its hydrophobic nature, the nonpolar portions of lipoproteins are inverted towards the inside of the protein complex. The polar side chains which soluble in the aqueous environment will face outwards so that it would be able to associate with the environment.
Saturated fat vs Unsaturated fat
Unsaturated fats contain one or more C=C (carbon-carbon double bonds) while saturated fats contain only C-C (carbon-carbon single bonds) in their long hydrophobic chain. The presence of C=C lead to ‘kinks’ within the fatty acid chains in the triglyceride molecule – which contribute to a lower melting point as the number of C=C in the molecule increases.
Fun fact:
Each gram of fat is able to release twice as much energy as the same mass (per gram) of carbohydrate.
References:
- http://thepaleodiet.com/fats-and-fatty-acids/
- http://science.howstuffworks.com/fatty-acids-info.htm
- http://kidshealth.org/kid/stay_healthy/food/fat.html
- http://scifun.chem.wisc.edu/chemweek/pdf/fats&oils.pdf
- http://www.healthknot.com/dietary_fats.html
- http://www.biotopics.co.uk/as/lipidcondensation.html
- http://nutritionrendition.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/06/lipoprotein.png
- http://www.elmhurst.edu/~chm/vchembook/551fattyacids.html
- http://www.humankinetics.com/excerpts/excerpts/the-bodyrsquos-fuel-sources
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fat#/media/File:Trimyristin-3D-vdW.png
- http://www.dummies.com/how-to/content/the-truth-about-fats-and-lipids.html
- http://www.infoplease.com/cig/biology/lipids.html
Given a choice, would you eat more carbohydrates or fats?
