Fossil fuels consist of oil coal, and natural gas. Fossil fuels are non-renewable resources, meaning that once our fossil fuel resources run out, it will take many lifetimes for these sources to be replenished (National Geographic, n.d). Energy is obtained from fossil fuels by burning them. This process releases greenhouse gases – carbon dioxide, nitrate oxides, and sulfur dioxide – into the atmosphere (Environmental and Energy Study Institute, 2014)b. Greenhouse gases trap heat when released into the atmosphere, retaining heat from the sun to keep the earth warm and suitable for us to live in. This process is known as the greenhouse effect, and is illustrated in the figure below.
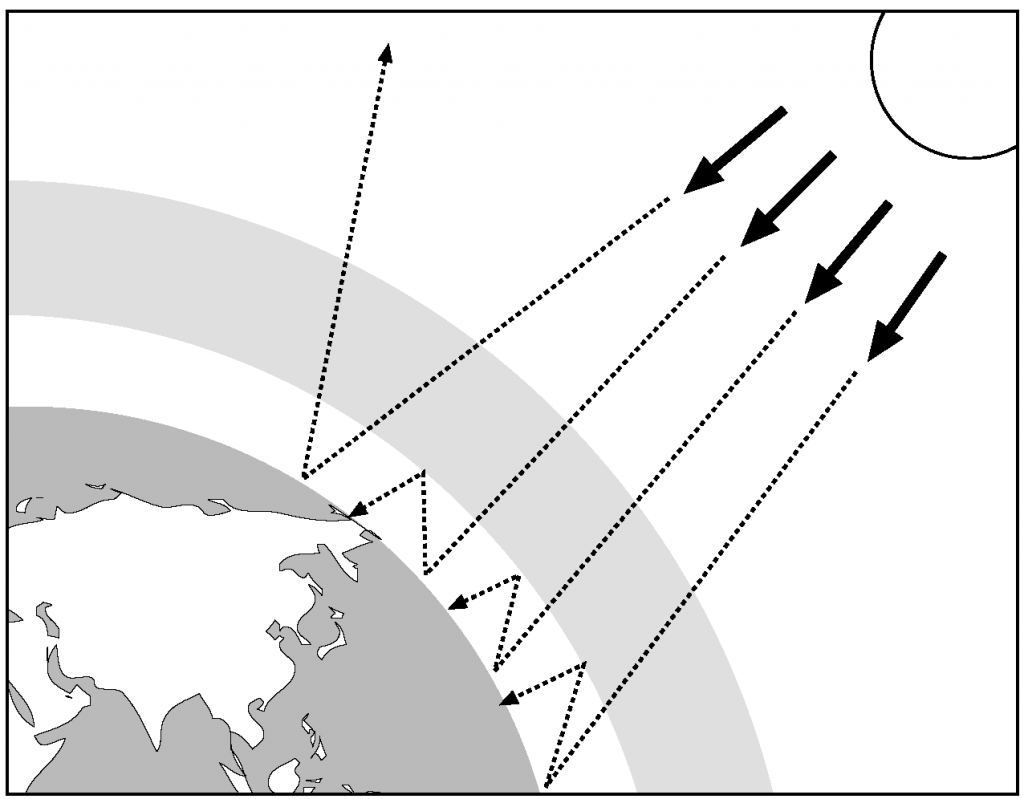
Figure 1. Illustration of greenhouse effect. Retrieved from http://www.rsc.org/learn-chemistry/wiki/images/a/a9/GreenhouseEffectDiagram01.png
However, with the massive release of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere from our energy consumption, a lot more heat is retained in the earth’s atmosphere. This contributes to global warming, which is the rise in average surface temperature of the earth.
To learn more about the different types of fossil fuels, please click on the respective tabs above. 🙂