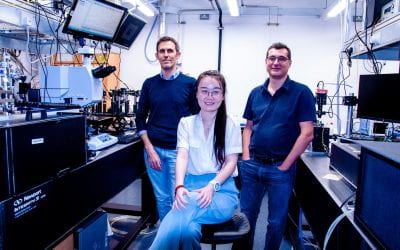
Using optical fibres, physicists form particles whose masses are generated by energy non-conservation.
Electrons Through The Looking Glass
Researchers have developed new materials called higher-fold chiral semimetals, with unusual properties coming from the intrinsic chirality or “handedness” of their electrons.
Electron Liquids on the Cutting Edge
A team led by Assistant Professor Bent Weber uses state-of-the-art microscopy techniques to study and control one-dimensional electron fluids, with the aim of creating robust quantum computers.
Mathematical AI Methods Supercharge the Search for Perovskite Materials
New artificial intelligence techniques are applied to the design of perovskite materials, predicting their properties with unprecedented accuracy and efficiency.
Nanostructured perovskites add a twist to light
Using nanostructured perovskite materials, scientists have created optical devices with greatly enhanced ability to absorb or emit chiral light.
SPRUCE: Sustainable Plastics RepUrposing for a Circular Economy
Researchers at NTU’s School of Physical and Mathematical Sciences are attempting to implement large-scale “upcycling” of plastic waste, using renewable energy to convert it into chemical feedstocks.
Mixing light and matter in 2D materials
Using a two-dimensional material, physicists can generate and control exciton polaritons, particles composed of light and matter, at ambient temperatures.
A new method for creating sulphur-based medicines
A key technical challenge in creating new sulphur-based medicines has been overcome by scientists at Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore), leading to the prospect of many new therapeutic ‘weapons’ in the fight against disease and illness.
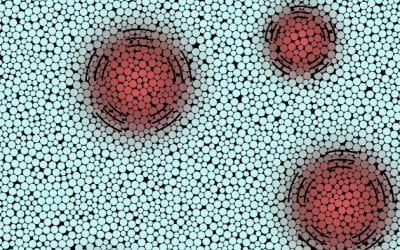
Disordered Solids Give Off Strange Vibes
Using numerical simulations, two physicists have explained some long-standing anomalies in the behaviour of sound waves in disordered materials.
Looking For Relationships (in a Big Data Stream)
Assistant Professor Li Yi and his collaborators have found a new way to calculate correlations in very large data sets, providing an exponential improvement over earlier algorithms.