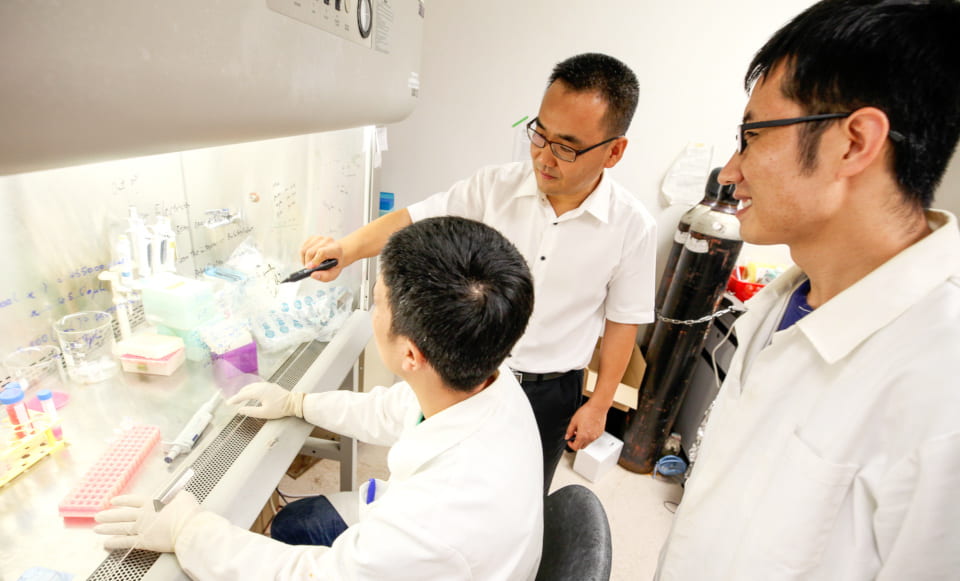
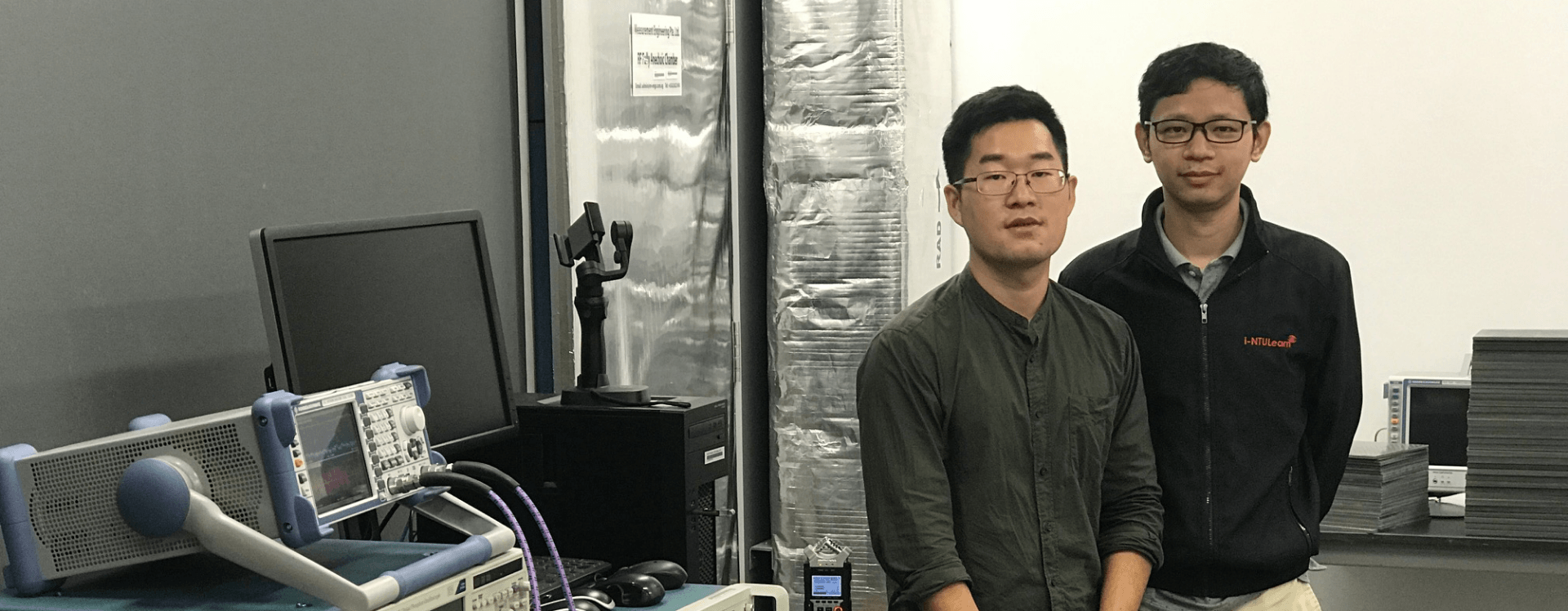
The research group of Professor Weibo Gao has performed the first experimental measurement of “quantum curvature” in a material, paving the way for novel quantum materials.
Electrons Through The Looking Glass
Researchers have developed new materials called higher-fold chiral semimetals, with unusual properties coming from the intrinsic chirality or “handedness” of their electrons.
Blending Superconductivity and Magnetism to Create New Quantum Particles
Physicists have created a hybrid material in which superconductivity and magnetism interact, which could be used to create a new type of quantum computer.
The First Electrically-Driven Topological Laser
Scientists and engineers from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU) and the University of Leeds in the UK have created the first electrically-driven ‘topological’ laser — a device that can route light waves around corners and cope with defects introduced in the manufacture of the device.
Solvent-Free Synthesis of Advanced Materials
When thinking of chemists at work, we usually visualize them mixing liquids in vials and test tubes. This approach to chemistry, working with reagents dissolved in organic solvents such as ethanol or dichloromethane, is called solution synthesis. While common, it is not the only game in town; another set of techniques known as mechanochemistry, which involves directly mixing chemicals in their undiluted forms, is emerging as an environmentally friendly way to create state-of-the-art chemicals.
Detecting Disease Through the Interplay of Light and Sound
In modern medicine, doctors can use a variety of technologies to peer inside their patients to detect and monitor the signs of disease. Methods such as X-ray imaging and ultrasound imaging are well known to the public, but researchers are also developing new imaging methods of unprecedented speed and sensitivity, by creatively combining ideas from physics, chemistry, and biology. Read more
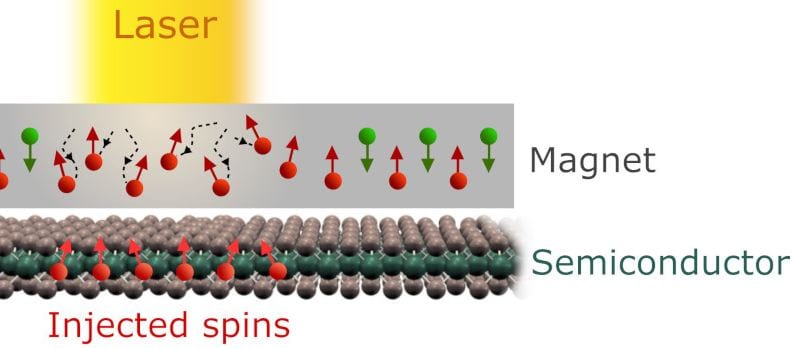
A decisive step towards ultrafast spintronics
Electronics has revolutionized the modern world, owing to continuous improvements in microprocessor technology since the 1960s. However, this process of refinement is projected to stall in the near future, due to constraints imposed by the laws of physics. Some of these bottlenecks have already taken effect: for instance, the clock rate (the rate at which transistors perform digital operations) has been unable to exceed a few gigahertz, or several operations per nanosecond, for the past twenty years, a limitation stemming from the electrical resistance of silicon.
Scientists realize a 3D ‘topological’ medium for EM waves
Topological insulators are exotic states of matter that physicists have been intensely studying for the past decade. Their most intriguing feature is that they can be rigorously distinguished from all other materials using a mathematical concept known as “topology”. This mathematical property grants topological insulators the ability to transport electric signals without dissipation, via special quantum states called “topological surface states”.