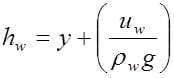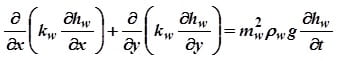Seepage Analyses
Seepage analyses are carried out to obtain the variations of pore-water pressures during and after rainfall. Parameters required for seepage analyses are: (i) slope geometry, (ii) flux boundary conditions (rainfall, evaporation), (iii) initial condition (groundwater table), (iv) soil-water characteristic curve (SWCC), (v) permeability function (kw).
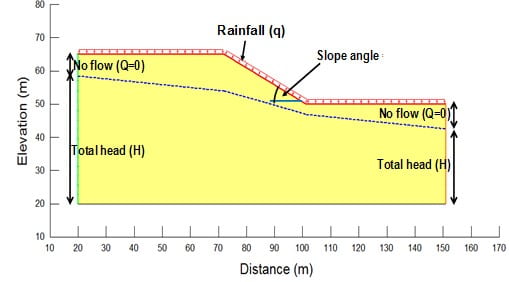
Finite element seepage model to study the effect of rainfall and evaporation on slope stability, Rahardjo et al 2010
Flow law for water (Darcy’s law)
Saturated soil, Darcy 1856
Unsaturated soil, Fredlund and Rahardjo 1993
Unsteady-state water seepage in an unsaturated/ saturated soil, Richards 1931
References
- Rahardjo, H., Satyanaga, A. and Leong, E. C. (2013). “Effects of flux boundary conditions on pore-water pressure distribution in slope.” Journal of Engineering Geology, Special Issue on Unsaturated Soils: Theory and Applications, October, 165, 133-142. doi | handle
- Rahardjo, H., Satyanaga, A., Leong, E. C. and Ng, Y. S. (2010). “Effects of groundwater table position and soil properties on stability of slope during rainfall.” ASCE Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering. November, 136(11), 1555–1564. doi | handle
- Rahimi, A., Rahardjo, H. and Leong, E. C. (2010). “Effect of hydraulic properties of soil on rainfall-induced slope failure.” Journal of Engineering Geology, 114, 135-143. doi | handle
- Schnellmann, R., Busslinger, M., Schneider, H. and Rahardjo, H. (2010). “Effect of rising water table in an unsaturated slope.” Journal of Engineering Geology, 114, 71-83. doi | handle
- Rahardjo, H., Ong, T. H., Rezaur, R. B., Leong, E. C. and Fredlund, D. G. (2010). “Response parameters for characterization of infiltration.” Environmental Earth Sciences, 60(7), 1369 – 1380. doi | handle
- Rahardjo, H., Leong, E. C. and Rezaur, R. B. (2008). “Effect of antecedent rainfall on pore-water pressure distribution characteristics in residual soil slopes under tropical rainfall.” Hydrological Processes, Special Issue on Rainfall Induced Landslides and Debris Flow, 22, 506-523. doi | handle
- Rahardjo, H., Ong, T. H., Rezaur, R. B. and Leong, E. C. (2007). “Factors controlling instability of homogeneous soil slopes under rainfall loading.” ASCE Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering. December, 133(12), 1532-1543. doi | handle
- Rezaur, R. B., Rahardjo, H., Leong, E. C. and Lee, T. T. (2003). “Hydrologic behaviour of residual soil slopes in Singapore.” ASCE Journal of Hydrologic Engineering. May/June, 8(3), 133-144. doi | handle
- Rezaur, R. B., Rahardjo, H. and Leong, E. C. (2002). “Spatial and temporal variability of pore-water pressures in residual soil slopes in a tropical climate.”Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, March, 27, 317-338. doi | handle
- Tsaparas, I., Rahardjo, H., Toll, D. G. and Leong, E. C. (2002). “Controlling parameters for rainfall-induced landslides.” Computer and Geotechnics, January, 29(1), 1-27. doi | handle
- Rahardjo, H., Li, X. W., Toll, D. G. and Leong, E. C. (2001). “The effect of antecedent rainfall on slope stability.” Journal of Geotechnical and Geological Engineering, Special Issue on “Unsaturated and Collapsible Soils,” September, 19(3-4), 371-399. doi | handle
- Gasmo, J. M., Rahardjo, H. and Leong, E. C. (2000). “Infiltration effects on stability of a residual soil slope.” Computer and Geotechnics, 26, April, 145 – 165. doi | handle
- Fredlund, D. G. and Rahardjo, H. (1993). Soil mechanics for unsaturated soils, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 517 pages (ISBN 0-471-85008-X). doi
- Richards, L. A. (1931). “Capillary conduction of liquids through porous mediums”. Physics 1(5), 318–333. doi
- Darcy, H. (1856). Les Fontaines Publiques de la Ville de Dijon. Dalmont, Paris. Google books