- Slope Instrumentation
- Instrumentation Reading
- Evaporation
- Variations in Groundwater Table
- Case Studies
The early research collaboration between NTU and Public Works Department (PWD), funded by National Science and Technology Board (NSTB), established guidelines for the stability assessments against rainfall-induced slope failures. The site investigation procedures and the laboratory testing protocols for soil characterization in Singapore were developed throughout this project
Location of instrumented residual soil slope in Singapore, Rahardjo et al 2014
- Ang Mo Kio
- Bedok
- Jalan Kukoh
- Lorong Halus
- Mandai
- Marsiling
- NTU-ANX
- NTU-CSE
- Pasir Ris
- Tampines
- Telok Blangah
- Yishun
Slope Instrumentation Layout and Field Plot
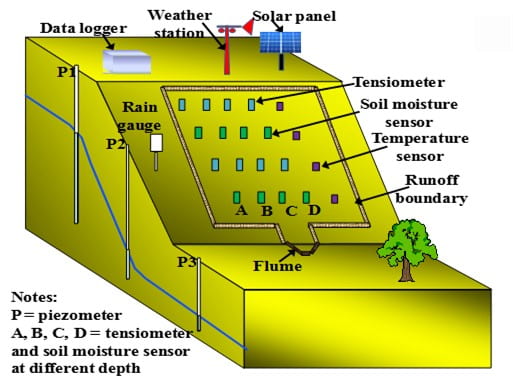
Typical layout of slope instrumentation, Rahardjo et al 2004

Field plot for studying rainfall, runoff and infiltration processes at NTU-CSE slope, Tsaparas et al 2003

Field installation of a flume with water depth probe for runoff measurement at NTU-CSE slope, Tsaparas et al 2003

Runoff measurement results from field study at NTU-CSE slope, Rahardjo et al 2004

Schematic diagram of an open double-ring infiltration test, Indrawan et al 2006

Percentage of infiltration as a function of rainfall amount, Rahardjo et al 2013
Schematic diagram of on-line monitoring system, Rahardjo et al 2014
Relationship of increase in pore-water pressure at 50 cm depth to daily rainfall amount for residual slopes in Singapore, Rahardjo et al 2007
References
- Rahardjo, H., Satyanaga, A., Leong, E. C. and Wang, J. Y. (2014). “Comprehensive instrumentation for real time monitoring of flux boundary conditions in slope.” Procedia Earth and Planetary Science, August, 9, 23-43.doi
- Rahardjo, H., Satyanaga, A., Leong, E. C., Santoso, V. A. and Ng, Y. S. (2014). “Performance of an instrumented slope covered with shrubs and deep rooted grass.” Soils and Foundations, Japanese Geotechnical Society, May, 54(3), 417-425. doi
- Rahardjo, H., Satyanaga, A. and Leong, E. C. (2013). “Effects of flux boundary conditions on pore-water pressure distribution in slope.” Journal of Engineering Geology, Special Issue on Unsaturated Soils: Theory and Applications, October, 165, 133-142. doi | handle
- Rahardjo, H., Santoso, V. A., Leong, E. C., Ng, Y. S. and Hua, C. J. (2012). “Performance of an instrumented slope covered by a capillary barrier system.” ASCE Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering,April, 138(4), 481 – 490. doi| handle
- Rahardjo, H., Satyanaga, A. and Leong, E. C. (2012). “Unsaturated soil mechanics for slope stabilization.” Southeast Asian Geotechnical Journal, March, 43(1), 48-58.
- Rahardjo, H., Santoso, V. A., Leong, E. C., Ng, Y. S. and Hua, C. J. (2011). “Numerical analyses and monitoring performance of residual soil slopes.” Soils and Foundations, Japanese Geotechnical Society, June, 51(3), 471-482. doi| handle
- Rahardjo, H., Satyanaga, A., Leong, E. C. (2007). “Characteristics of pore-water pressure response in slopes during rainfall.” Proceedings of 3rd Asian Conference on Unsaturated Soils, Nanjing, China, 21-23 April, 493-498. handle
- Indrawan, I. G. B., Rahardjo, H., Leong, E. C. (2006). “Study of infiltration characteristics in the field.” Proceedings of 4th International Conference on Unsaturated Soils, Geo Institute. Phoenix, Arizona, U.S.A., 2-5 April, 179–190.doi
- Rahardjo, H., Lee, T. T., Leong, E. C. and Rezaur, R. B. (2005). “Response of a residual soil slope to rainfall.” Canadian Geotechnical Journal, April, 42(2), 340-351. doi| handle
- Rahardjo, H., Lee, T. T., Leong, E. C. and Rezaur, R. B. (2004). “A flume for assessing flux boundary characteristics in rainfall-induced slope failure studies.” Geotechnical Testing Journal, ASTM International, March, 27(2), 145–153. AWARD PAPER for “Outstanding Article on the Practice of Geotechnical Testing.” doi | handle
- Tsaparas, I., Rahardjo, H., Toll, D. G. and Leong, E. C. (2003). “Infiltration characteristics of two instrumented residual soil slopes.” Canadian Geotechnical Journal, October, 40(5), 1012–1032. doi | handle
- Gasmo, J. M., Hritzuk, J. K., Rahardjo, H. and Leong, E. C. (1999). “Instrumentation of an unsaturated residual soil slope.” Geotechnical Testing Journal, ASTM International, 22(2), June, 134-143. doi| handle
- Lim, T. T., Rahardjo, H., Chang, M. F. and Fredlund, D. G. (1996). “Effect of rainfall on matric suction in a residual soil slope.” Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 33, 618-628. doi | handle
Field Instrumentation

 Type of tensiometer used in residual soil slope in Singapore, Rahardjo et al 2011
Type of tensiometer used in residual soil slope in Singapore, Rahardjo et al 2011

 Soil moisture sensor for monitoring of water content at residual soil slope in Singapore, Rahardjo et al 2011
Soil moisture sensor for monitoring of water content at residual soil slope in Singapore, Rahardjo et al 2011


Weather station for measurement of rainfall and evaporation, Rahardjo et al 2011



