Tidal energy is a type of hydropower that converts power of tides into other useful forms of power, mainly electricity. Tides are the rise and fall of the sea levels which were resulted from gravitational effect of the moon circulating the earth and the rotation of the earth itself. This makes tidal energy more predictable than other forms of renewable energy such as solar energy or wind energy.
There are 3 ways to generate tidal energy:
- Tidal stream uses the kinetic energy of flowing water to power the water turbine, much as wind turbines extract energy from the movement of air.
- Tidal barrage captures the potential energy from the difference between the heights of different tides using specialized dams called barrage. These dams are opened when the water is rising and closed when the water is at peak. When the water goes low, the dams are opened again, allowing water to flow through the turbines.
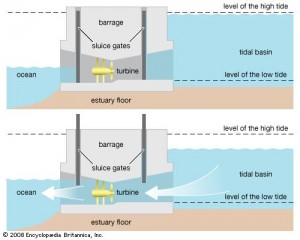
Tidal Barrage - Tidal lagoon uses manmade or natural pools of ocean water that is partially cut off from the ocean by a barrier, which are called lagoons. This method works much like tidal barrage; however, tidal lagoons can be constructed naturally.
Reference
- Kim Rutledge, M. M. (2015, March 20). Tidal Energy. Retrieved from National Geographic Education: http://education.nationalgeographic.com/education/encyclopedia/tidal-energy/?ar_a=1