1) Understanding Earth’s energy balance is essential to understanding the issue of global warming. For example, the solar energy striking Earth’s surface averages 168 W/m2,but the energy leaving earth surface averages 390 W/m2. Why isn’t Earth cooling rapidly?
This is primarily due to Greenhouse Effect. Greenhouse effect is due to heat trapped by the greenhouse gases such as CO2, N2O and CH4. The greenhouse gases radiates the heat back to earth and causes a heating effect which leads to a rise in global temperatures. The concentration of greenhouse gases has also increased dramatically over the years, which causes the trapping of greenhouse gases and greenhouse effect is enhanced, leading to an overall heating effect rather than cooling effect.
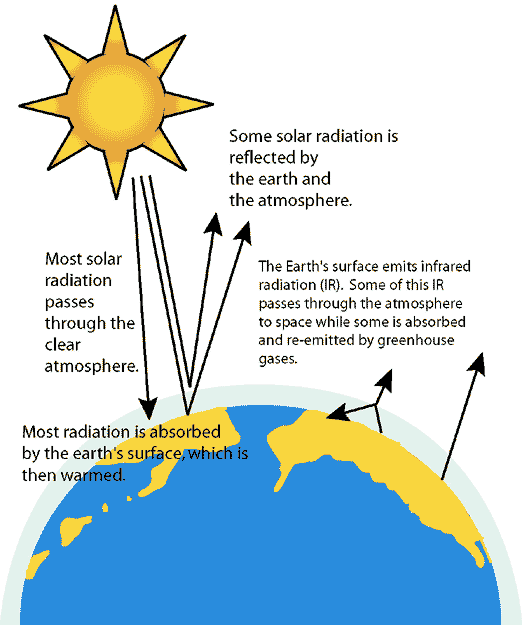
Greenhouse effect explained
2) Do you think the statement made by the cartoon is justified ? Explain.

It is not justified. Global warming is a trend that describes global temperatures have risen over the years. While extreme climates is believed to be linked to global warming. Melting of ice caps due to global warming has disrupted the normal course of ocean circulation; which regulates global temperature. This disruption has since caused more frequent extreme cold weathers especially in areas such as Europe. Furthermore, Global warming is also linked to shorter duration of winter. Therefore, the cartoon is not justified.
3) One of the first radar devices developed during the World War II used microwave radiation of a specific wave range that triggers the rotation of water molecules. Why was the design not successful?
Radar is an equipment that transmit information/signal over very long distance. Microwave radiation has a low frequency and a moderate wavelength as compared to visible light and infra red, however, the wavelength is not long enough to travel though long distances. Furthermore, the energy of the microwave radiation is likely to be absorbed by the molecules that came into contact with it hence, the information might be lost if there is any interference. Therefore, the design with microwave radiation was unsuccessful.
4) Now that you have studied air quality (Unit 1), stratospheric ozone depletion (Unit 2), and global warming(Unit 3) which do you believe poses the most serious problem for you in the short run? In the long run?
Given that Singapore is a small developed country, in the short run, the most serious problem would be air quality. Singapore faces annual haze from the Indonesia forest fires that produces pollutants which clouds Singapore in a haze. This can cause breathing
difficulties and other health problems, leading to increased coughing or other serious problems in those who have breathing difficulties. This is a recurring problem every year in Singapore and will cause the most problems.
However, in the long run, we will feel the effects of global warming especially with global temperature estimated to rise by 4 degrees by the end 2100. This will definitely have a ripple effect and caused a long term problem for the earth in the near future.


