Introduction
Another issue apart from pollution is energy conservation. As our energy resources are depleting, it is important for us to conserve energy. In Singapore where there are no fossil fuels, energy conservation is even more of an issue to us.
Explanation
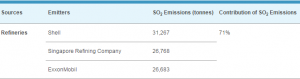
In April 2013, the Energy Conservation Act (ECA) took effect in Singapore. The Energy Conservation Act aims to provide an impetus to large industrial consumers to increase their energy efficiency and reduce the impact of their greenhouse gas emissions. Large energy consuming companies are also required to adopt energy management practices so that the government can look into their problems.
References
Mandatory Energy Management Practices. (n.d.). Retrieved on March 27, from http://www.nea.gov.sg/energy-waste/energy-efficiency/industry-sector/mandatory-energy-management-practices
Ghadialy, S. (2014). Retrieved on March 27, from http://www.greenbusiness.sg/2014/03/27/singapores-energy-conservation-act-what-it-means-for-companies/